Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), largely comprising the two conditions, Crohn’s
Disease and Ulcerative Colitis, is now emerging as a global health problem. It now affects
about 6 million people in Europe and US, comprising up to 620,000 in the UK
(IBD Standards UK,
2013 Update). The symptoms of diarrhoea, abdominal pain and bloody stool substantially
affect the quality of life of sufferers, and complications can be life threatening.
IBD is also strongly associated with colorectal cancer development risk.
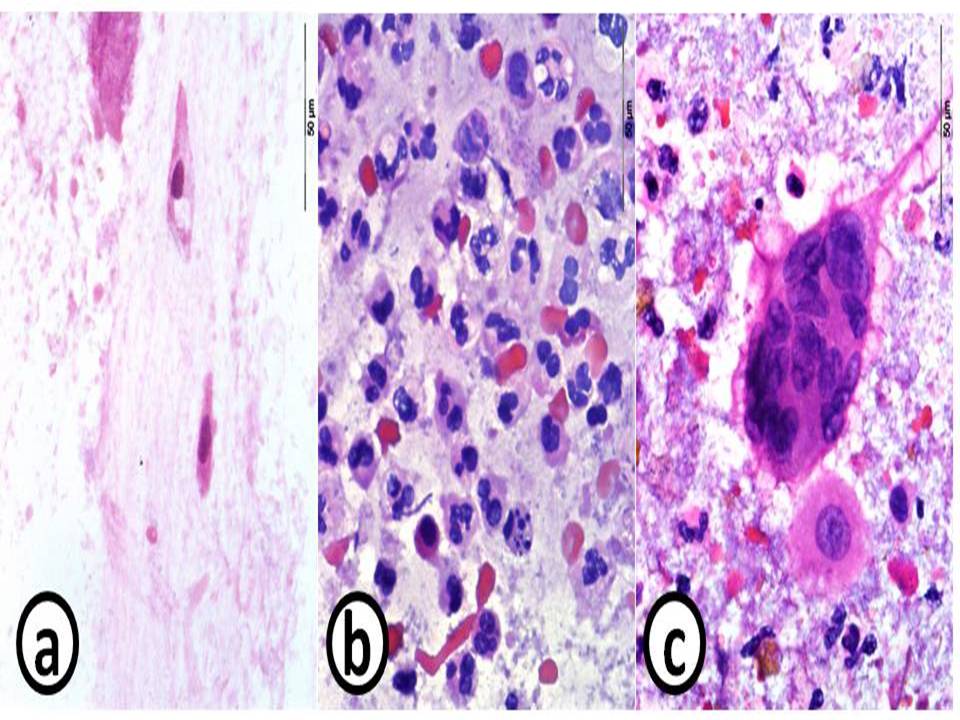
Cytological appearance of samples collected using the DiagNodus method from a
healthy volunteer (a) and patients with ulcerative colitis (b) and Crohn's disease (c)
The DiagNodus approach currently provides a simple, self-applied method for
colorectal sample collection and reliable tests for determining bowel inflammation activity.
These innovative techniques have been shown to be efficient for detecting IBD and
distinguishing patients suffering from IBD from individuals with irritable bowel syndrome
(a very common functional disorder producing similar symptoms). In addition, the DiagNodus
technology can be used for assessing therapy effect in IBD patients who are undergoing
treatment and monitoring those who are in remission (for detecting new disease flare-ups
early).
Having established and clinically evaluated a range of tests involving laboratory
analysis, the company is now developing a family of rapid point of care (POC) tests for IBD.
Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common cancer all over the world.
About 1.8 million new CRC cases were diagnosed globally in 2018, mostly in
developed countries.
The incidence of colorectal cancer is increasing in line with the ageing
population. Early detection is key to successful treatment of the disease and
related cost management. An efficient screening strategy is essential to detect
the disease early, when it often does not produce symptoms. The currently available
faecal occult blood test (FOBT) and faecal immunochemical test (FIT) are safe and inexpensive, but test sensitivities
are limited, and the required stool collection is inconvenient. Screening colonoscopies are popular
in the US, but they are expensive to perform, extremely invasive and can sometimes cause
serious complications.
The DiagNodus approach to the CRC detection is based upon measuring CRC biomarkers
captured on a swab device self-applied by the patient. The adoption of the approach
would still require confirmatory diagnostic colonoscopies, but CRC detection rate
should be considerably improved and numbers of unnecessary colonoscopies dramatically
reduced.
DiagNodus has successfully completed its first clinical study targeting CRC in 2018,
and is ready to develop a new commercial product for CRC detection.
Future Applications
The colorectal sampling system developed by DiagNodus allows non-invasively
collecting highly informative samples suitable for detecting a number of other
important diseases.
In particular, collected colorectal mucus is a habitat of commensal microorganisms
that are extremely important for normal functioning of the human gut. Therefore the
use of this material in combination with modern microbiomic techniques can lead to
the development of new diagnostic modalities for a range of common gastrointestinal
diseases, especially diarrhoeas. This approach may also be very useful for
investigating microbiome-associated causes of such general chronic conditions as
autoimmune diseases, obesity and diabetes.

